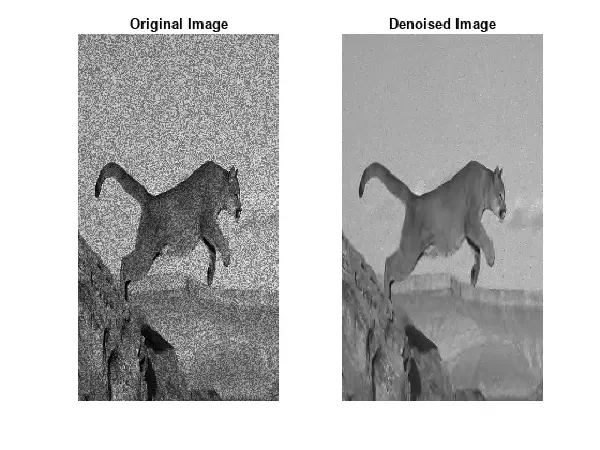
In the vast realm of image processing, one of the paramount challenges is combating noise that obscures the essence of digital visuals. Image denoising, a sophisticated technique rooted in the realm of computer vision, is the beacon that guides us through the pixelated labyrinth.
In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of image denoising, exploring the underlying principles, methodologies, and transformative impact it can have on enhancing visual clarity.
Unmasking the Noise
Understanding Image Noise
Before we embark on the journey of denoising, it’s crucial to comprehend the adversary – image noise. Noise, akin to visual interference, introduces unwanted variations, blurring the lines between reality and distortion. This noise can emanate from various sources, such as sensor limitations, compression artifacts, or environmental factors.
The Denoising Imperative
The fundamental goal of image denoising is to unravel the concealed details within a noise-ridden image. It’s akin to restoring an old painting, bri denoised_image = cv2.fastNlMeansDenoisingColored(image, None, h=10, hColor=10, templateWindowSize=7, searchWindowSize=21) nging back the vibrancy and precision that noise tends to erode. By suppressing the unwanted visual clutter, denoising reclaims the true essence of the image.
The Symphony of Denoising Techniques
Traditional Methods
Historically, denoising relied on traditional signal processing techniques like median filtering or Gaussian smoothing. While effective to some extent, these methods often fall short in preserving fine details, leaving a trade-off between noise reduction and image fidelity.
Enter OpenCV
OpenCV, the open-source computer vision library, emerges as a pivotal player in the contemporary denoising landscape. Leveraging powerful algorithms, OpenCV provides a suite of functions specifically designed for image denoising. The cv2.fastNlMeansDenoising() and cv2.fastNlMeansDenoisingColored() functions are exemplary tools in the denoising arsenal, capable of striking a delicate balance between noise reduction and feature preservation.
A Glimpse into the Denoising Algorithms
Non-Local Means Denoising
At the heart of OpenCV’s denoising capabilities lies the non-local means (NLM) algorithm. This ingenious approach harnesses the redundancy within an image, exploiting similarities between patches rather than individual pixels. By gauging the resemblance between different image regions, NLM achieves a nuanced denoising effect, adept at handling diverse noise profiles.
Deep Learning Revolution
In recent years, the advent of deep learning has ushered in a new era for image denoising. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) like U-Net and autoencoders have demonstrated remarkable prowess in discerning and eliminating noise patterns. Trained on vast datasets, these networks can decipher complex relationships within an image, outshining traditional methods in both speed and precision.
Integrating Image Denoising into Your Workflow
Step-by-Step Implementation with OpenCV
Import OpenCV:
import cv2Read Image:
image = cv2.imread('noisy_image.jpg')Apply Denoising:
denoised_image = cv2.fastNlMeansDenoisingColored(image, None, h=10, hColor=10, templateWindowSize=7, searchWindowSize=21)Display Results:
cv2.imshow('Original Image', image) cv2.imshow('Denoised Image', denoised_image) cv2.waitKey(0) cv2.destroyAllWindows()
**Conclusion 🏁 **
In the ever-evolving landscape of image processing, image denoising stands as a stalwart guardian against the infiltrating forces of noise. Whether you opt for traditional methods or embrace the cutting-edge capabilities of OpenCV and deep learning, the goal remains steadfast – to reveal the true beauty hidden beneath the pixelated veil. As you embark on your denoising endeavors, may your images be pristine and your visual narratives untarnished. Happy denoising!