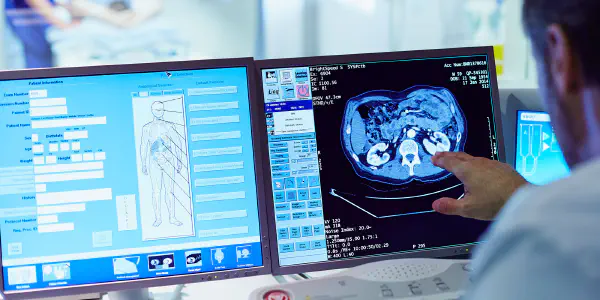
Computer-aided detection (CAD) systems are software programs designed to assist radiologists in detecting and diagnosing abnormalities in medical images. CAD systems can be used for a variety of medical imaging modalities, including mammography, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
How do CAD systems work?
CAD systems typically work by analyzing the pixel intensity values of medical images. They use algorithms to identify patterns and features that are indicative of abnormalities. CAD systems then mark these areas of interest for the radiologist to review.
Benefits of CAD systems
There are several benefits to using CAD systems:
1. Increased detection accuracy: CAD systems can help to improve the detection of abnormalities by identifying subtle features that may be missed by the naked eye.
2. Reduced reading time: CAD systems can help radiologists to read medical images more quickly and efficiently.
3. Improved patient care: By helping to improve the detection and diagnosis of abnormalities, CAD systems can lead to improved patient care.
Types of CAD systems
There are two main types of CAD systems:
Computer-aided detection (CADe) systems: CADe systems are designed to detect abnormalities in medical images.
Computer-aided diagnosis (CADx) systems: CADx systems are designed to diagnose abnormalities in medical images.
Examples of CAD systems
There are a number of commercially available CAD systems for different medical imaging modalities. Some examples include:
Mammography CAD systems: These systems are designed to detect breast cancer in mammograms.
CT CAD systems: These systems are designed to detect lung nodules and other abnormalities in CT scans.
MRI CAD systems: These systems are designed to detect brain tumors and other abnormalities in MRI scans.
The future of CAD systems
CAD systems are a rapidly evolving technology. With the development of new algorithms and machine learning techniques, CAD systems are becoming increasingly accurate and sophisticated.
Conclusion 🏁
CAD systems are a valuable tool for radiologists, helping to improve the detection and diagnosis of abnormalities in medical images. As CAD technology continues to develop, it is likely to play an even greater role in the future of medical imaging.
Here are some additional points to consider:
- CAD systems are not intended to replace radiologists. They are meant to be used as a tool to assist radiologists in their work.
- It is important to use CAD systems with caution. CAD systems can sometimes generate false positives, which can lead to unnecessary patient anxiety and testing.
- Radiologists should always carefully review the areas of interest marked by CAD systems before making a diagnosis.