In today’s automotive industry, safety is paramount. Manufacturers are constantly innovating to develop new technologies that enhance the driving experience and reduce the risk of accidents. One of the most promising advancements in this area is the integration of computer vision into advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
ADAS is a broad term encompassing a range of electronic systems designed to assist drivers in various aspects of vehicle operation. These systems can provide warnings, alerts, and even automated interventions to help prevent collisions, improve lane positioning, and enhance overall driving safety.
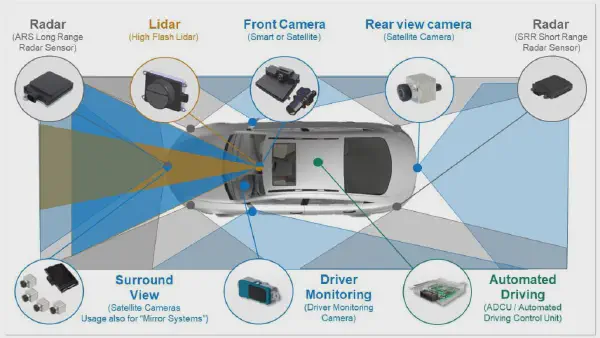
Traditionally, ADAS has relied on sensors like radar, lidar, and ultrasonic to gather information about the surrounding environment. However, the introduction of computer vision has opened up a new dimension of data and capabilities.
Computer Vision: Enhancing ADAS with Visual Intelligence
Computer vision, a branch of artificial intelligence, enables machines to interpret and understand visual information from the world around them. In the context of ADAS, computer vision algorithms can analyze images and video feeds from cameras mounted on the vehicle to identify and track objects, such as other vehicles, pedestrians, lane markings, traffic signs, and road conditions.
This visual intelligence empowers ADAS systems to perform a wide range of tasks, including:
1. Lane Departure Warning (LDW): Detecting lane markings and alerting the driver when the vehicle unintentionally strays from its lane.
2. Forward Collision Warning (FCW): Monitoring the distance to the vehicle ahead and alerting the driver of a potential collision.
3. Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB): Automatically applying brakes to prevent or mitigate a collision.
4. Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC): Maintaining a safe distance from the vehicle ahead and automatically adjusting speed accordingly.
5. Traffic Sign Recognition (TSR): Identifying and displaying traffic signs, such as speed limits and stop signs, to keep the driver informed.
6. Pedestrian Detection and Warning: Detecting and alerting the driver to the presence of pedestrians, especially in low-visibility conditions.
7. Night Vision Assistance: Enhancing the driver’s visibility in low-light conditions by processing images from infrared cameras.
Benefits of Computer Vision-Powered ADAS
The integration of computer vision into ADAS offers several significant benefits:
Improved Object Detection and Classification: Computer vision can identify and classify objects with greater accuracy and detail compared to traditional sensors, reducing false alarms and improving system reliability.
Enhanced Performance in Challenging Conditions: Computer vision can function effectively in various weather and lighting conditions, including nighttime, fog, and rain, where traditional sensors may struggle.
Real-time Processing for Timely Interventions: Computer vision algorithms can process visual data in real-time, enabling ADAS systems to react promptly and effectively to potential hazards.
Enabling New ADAS Features: Computer vision opens up possibilities for new ADAS features, such as driver drowsiness detection, traffic jam assistance, and autonomous parking.
Examples of Computer Vision-Powered ADAS Solutions
Several leading automotive technology companies are developing and deploying computer vision-powered ADAS solutions. Here are a few notable examples:
Mobileye’s EyeQ®: A comprehensive ADAS platform that utilizes computer vision and other sensors to provide a wide range of safety features.
Bosch ADAS Systems: A suite of ADAS solutions that includes lane departure warning, forward collision warning, and traffic sign recognition, all powered by computer vision.
Nvidia DriveWorks: An open-source ADAS software platform that provides computer vision libraries and algorithms for various ADAS applications.
Intel RealSense Technology: A combination of hardware and software that enables computer vision capabilities for ADAS applications, including pedestrian detection, object tracking, and depth perception.
The Future of Computer Vision-Powered ADAS
Computer vision is rapidly gaining traction in the ADAS landscape, and its role is expected to expand significantly in the future. As algorithms become more sophisticated and capable of handling a wider range of scenarios, computer vision will play an increasingly crucial role in developing autonomous vehicles and enhancing overall driving safety.
The integration of computer vision into ADAS is transforming the automotive industry, paving the way for a future of safer, more intelligent, and autonomous vehicles.